
How to Build Streaming Chat Apps with Convex's Plug-and-Play Components
Imagine building a ChatGPT-like streaming experience without wrestling with WebSockets or SSE protocols. With Convex Components, this becomes surprisingly simple. Let me show you how Convex Components simplifies the way we build real-time features.
If you’re a developer, you might already have a sense of what this means. The concept is similar to the component architecture used in frontend frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular, and it also resembles modular units found in backend frameworks like Spring or NestJS.
Convex goes beyond being just another server framework—it abstracts the entire client-server structure into modular, reusable components.
In other words, even backend logic is provided as declarative, reusable components, which is one of Convex’s most powerful features.

Source: Convex Components
From the official site, you can browse through all the components that have been pre-built by Convex.
For this tutorial, we’ll focus on @convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming. Unlike traditional APIs that return the full response at once, this component enables real-time streaming output, similar to how ChatGPT streams its responses.
Streaming provides a faster and more interactive user experience, as users can start seeing partial responses immediately instead of waiting for the entire message to complete.
Implementing this manually would usually require protocols like SSE or WebSockets, adding complexity. With Convex’s built-in component, you can skip the low-level implementation and quickly enable streaming functionality in your app.
Source: Persistent Text Streaming Component
The component interface shows how simple it is to implement streaming - just install, configure, and use the provided hooks.
To demonstrate this in action, we'll use Convex Chef to quickly spin up an AI chat feature. The complete code for this tutorial is available at https://github.com/hyochan/ai-chat.
After entering a prompt and waiting briefly, a fully functional React application is automatically generated. Notice how the generated app includes a chat interface ready for our streaming enhancement:
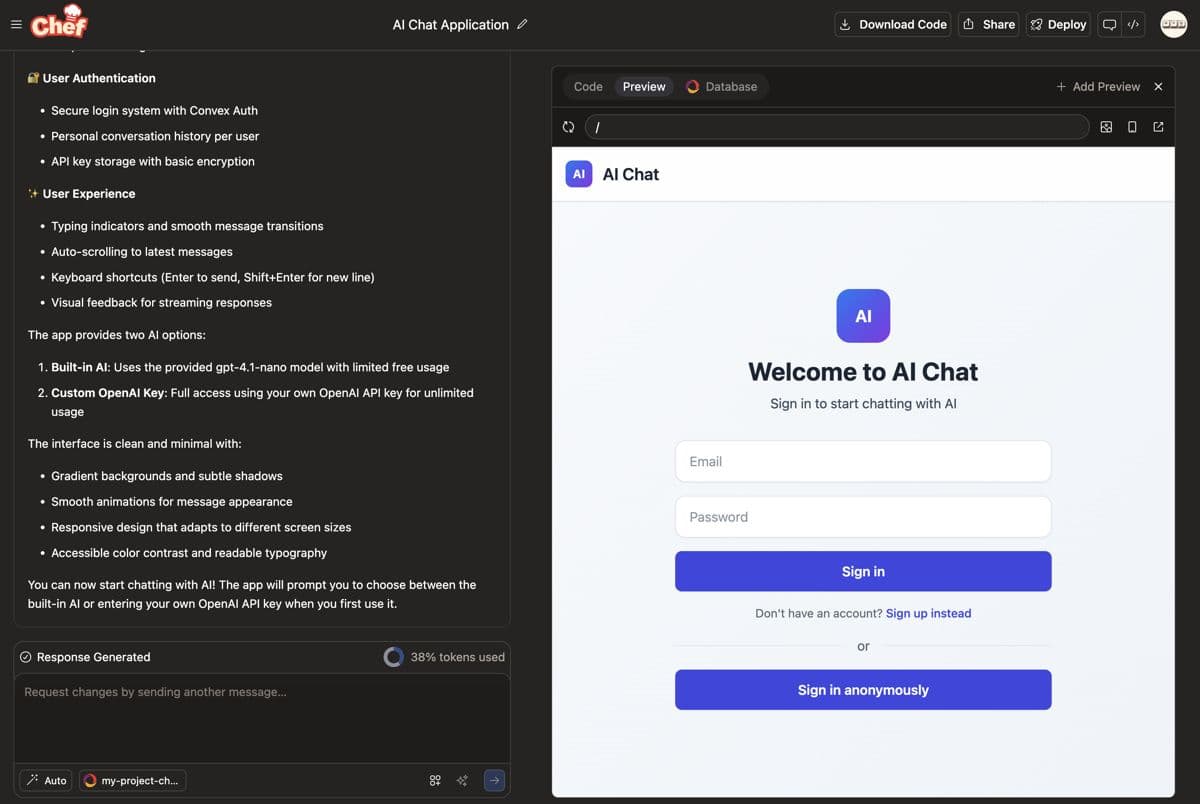
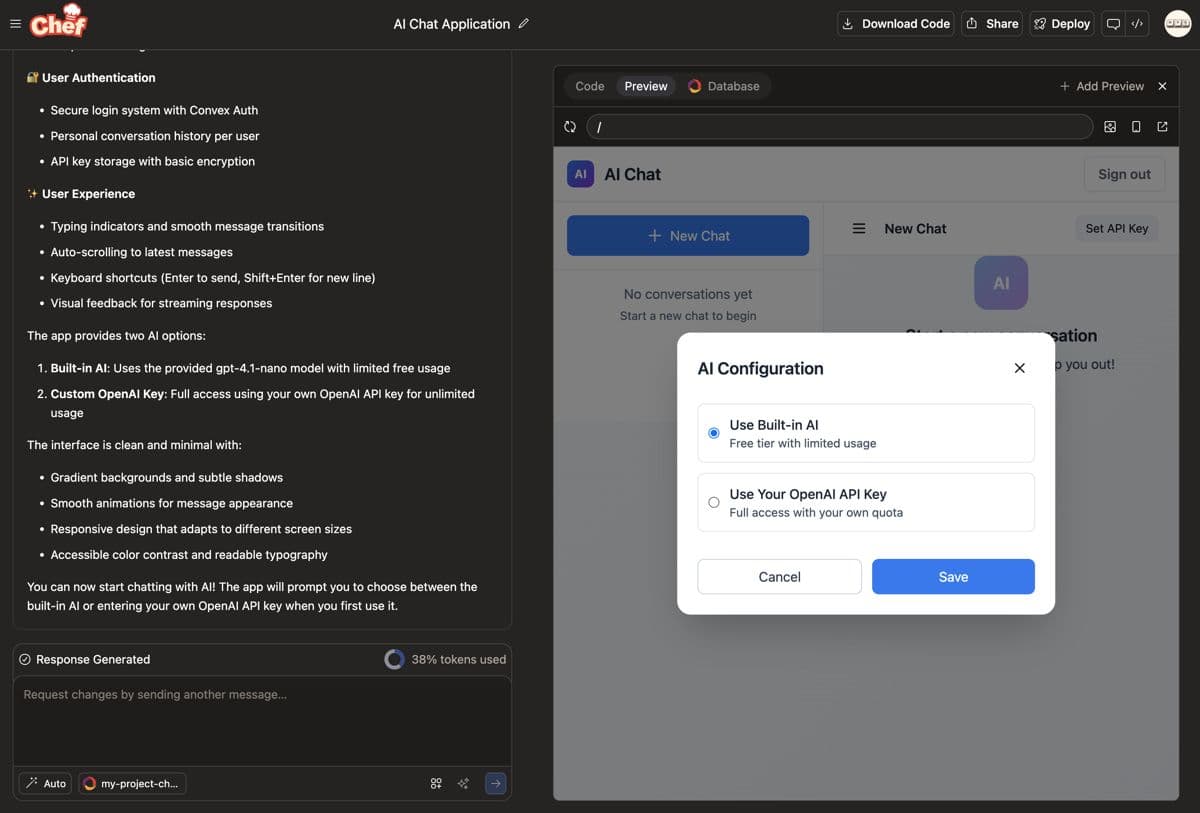
By clicking "Sign in anonymously", you can start chatting with AI. The interface shows messages in a traditional request-response pattern:
Currently, streaming is not yet enabled, so responses are delivered in full rather than progressively. Let’s integrate @convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming to enable real-time streaming functionality.
1. Setting up Persistent Text Streaming
Install the Package
1npm install @convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming
2Register the Component in Convex
1import { defineApp } from "convex/server";
2import persistentTextStreaming from "@convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming/convex.config";
3
4const app = defineApp();
5app.use(persistentTextStreaming);
6export default app;
7As described in the Convex documentation, defineApp() is a beta API that lets you define your Convex app by attaching reusable components. This allows you to modularly add functionalities like authentication, payments, or chat without manually setting up defineSchema and defineFunctions. Since it’s experimental, use it cautiously in production environments.
Set Up an HTTP Route
1import { httpRouter } from "convex/server";
2import { streamChat } from "./chat";
3
4const http = httpRouter();
5
6http.route({
7 path: "/chat-stream",
8 method: "POST",
9 handler: streamChat,
10});
11
12export default http;
13The streamChat handler accepts POST requests to /chat-stream and enables real-time text streaming. This endpoint will be used to stream AI responses back to the client.
2. Backend: Implementing Real-Time Streaming
Basic Streaming Pattern
Here’s a simple example that streams text one character at a time:
1import { PersistentTextStreaming } from "@convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming";
2import { StreamId } from "@convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming";
3import { components } from "./_generated/api";
4import { httpAction } from "./_generated/server";
5
6const persistentTextStreaming = new PersistentTextStreaming(
7 components.persistentTextStreaming
8);
9
10export const streamChat = httpAction(async (ctx, request) => {
11 const body = (await request.json()) as {
12 streamId: string;
13 conversationId: string;
14 userMessage: string;
15 };
16
17 const generateChat = async (ctx, request, streamId, chunkAppender) => {
18 try {
19 const message = "Hello! How can I help you today?";
20
21 // Stream the response character by character
22 for (let i = 0; i < message.length; i++) {
23 await chunkAppender(message[i]);
24 await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 50));
25 }
26 } catch (error) {
27 console.error("Chat generation error:", error);
28 await chunkAppender("Sorry, an error occurred.");
29 }
30 };
31
32 const response = await persistentTextStreaming.stream(
33 ctx,
34 request,
35 body.streamId as StreamId,
36 generateChat
37 );
38
39 // Set CORS headers
40 response.headers.set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
41 response.headers.set("Vary", "Origin");
42 return response;
43});
44PersistentTextStreaminginitializes the streaming component.generateChatfunction receives achunkAppenderto send text incrementally.persistentTextStreaming.stream()handles the HTTP streaming response.- CORS headers are set for cross-origin requests.
Complete Streaming Implementation
Here's the complete implementation that handles message history and streaming:
1export const streamChat = httpAction(async (ctx, request) => {
2 const body = (await request.json()) as {
3 streamId: string;
4 conversationId: string;
5 userMessage: string;
6 };
7
8 const generateChat = async (
9 ctx: any,
10 request: any,
11 streamId: StreamId,
12 chunkAppender: any
13 ) => {
14 try {
15 // Get the message that we're streaming to
16 const message = await ctx.runQuery(api.chat.getMessageByStreamId, {
17 streamId,
18 });
19 if (!message) {
20 await chunkAppender("Error: Message not found");
21 return;
22 }
23
24 // Get conversation history
25 const allMessages = await ctx.runQuery(api.chat.getMessagesInternal, {
26 conversationId: message.conversationId,
27 });
28
29 // Get the user's latest message
30 const userMessages = allMessages.filter((m: any) => m.role === "user");
31 const latestUserMessage = userMessages[userMessages.length - 1];
32
33 if (!latestUserMessage) {
34 await chunkAppender("Hello! How can I help you today?");
35 return;
36 }
37
38 // Generate AI response (this is where you'd integrate with OpenAI, Claude, etc.)
39 const userContent = latestUserMessage.content;
40 const response = `I received your message: "${userContent}". How can I help you further?`;
41
42 // Stream the response character by character
43 for (let i = 0; i < response.length; i++) {
44 await chunkAppender(response[i]);
45 await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 50));
46 }
47
48 // Mark the message as complete
49 await ctx.runMutation(api.chat.markStreamComplete, {
50 messageId: message._id,
51 finalContent: response,
52 });
53 } catch (error) {
54 console.error("Chat generation error:", error);
55 const errorMessage =
56 "Sorry, an error occurred while generating the response.";
57 await chunkAppender(errorMessage);
58 }
59 };
60
61 const response = await persistentTextStreaming.stream(
62 ctx,
63 request,
64 body.streamId as StreamId,
65 generateChat
66 );
67
68 // Set CORS headers
69 response.headers.set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
70 response.headers.set("Vary", "Origin");
71 return response;
72});
73Key features:
- Retrieves the streaming message using
streamId - Fetches conversation history for context
- Streams response character by character for visual effect
- Marks the message as complete when done
- Handles errors gracefully
3. Frontend: Using the useStream Hook
Once the backend is set up with the /chat-stream endpoint, we can connect it to the client. The @convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming/react package provides a useStream hook that automatically handles real-time data updates in your UI.
Basic Usage
Here's a simple example of how to display streaming text in a React component:
1import { useStream } from "@convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming/react";
2import { StreamId } from "@convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming";
3import { api } from "../../convex/_generated/api";
4
5interface Message {
6 _id: string;
7 conversationId: string;
8 role: "user" | "assistant";
9 content: string;
10 streamId?: string;
11 isStreaming?: boolean;
12}
13
14function StreamingMessage({ message }: { message: Message }) {
15 // Convex site URL for HTTP actions - convert .cloud to .site
16 const convexApiUrl = import.meta.env.VITE_CONVEX_URL;
17 const convexSiteUrl = convexApiUrl?.replace('.convex.cloud', '.convex.site') || window.location.origin;
18
19 // For newly created streaming messages, this component should drive the stream
20 const isDriven = message.isStreaming === true;
21
22 const { text, status } = useStream(
23 api.chat.getStreamBody,
24 new URL(`${convexSiteUrl}/chat-stream`),
25 isDriven, // Drive the stream if the message is actively streaming
26 message.streamId as StreamId
27 );
28
29 // Use streamed text if available and streaming, otherwise use message content
30 const displayText = (status === "streaming" && text) ? text : message.content;
31 const isActive = status === "streaming" || message.isStreaming;
32
33 return (
34 <div className="whitespace-pre-wrap break-words">
35 {displayText}
36 {isActive && (
37 <span className="inline-block w-2 h-5 bg-current opacity-75 animate-pulse ml-1" />
38 )}
39 </div>
40 );
41}
42- api.chat.getStreamBody → The Convex query function that retrieves stream content
- URL → Points to the Convex backend HTTP route. Note: Convex serves HTTP endpoints on
.convex.sitedomain, not.convex.cloud - isDriven → Controls streaming behavior based on
message.isStreaming:true: Automatically starts streaming when the message is actively streamingfalse: Stream remains paused when the message is not streaming
- streamId → A unique ID created by the backend when generating a streaming response
- displayText → Shows streamed text during streaming, falls back to message content otherwise
- isActive → Visual indicator shown when either streaming is active or message is marked as streaming
Manual Start (Driven Option)
You can set isDriven to false to start streaming manually, such as when a button is clicked:
1const isDriven = false; // Manual control
2
3const { text, status } = useStream(
4 api.chat.getStreamBody,
5 new URL(`${convexSiteUrl}/chat-stream`),
6 isDriven,
7 streamId as StreamId
8);
9
10// Since isDriven is false, streaming won't start automatically
11// You'll need to trigger it based on your app's logic
12- Automatic mode (isDriven: true): Starts immediately when data is available.
- Manual mode (isDriven: false): Stream remains paused until conditions change.
4. Linking Stream Creation and Consumption
To take full advantage of PersistentTextStreaming, the backend needs to issue a stream ID when creating a message, and the frontend uses that ID to subscribe to real-time responses.
1. Assigning a Stream ID in the Backend
When a user sends a message, you can store it and create an empty assistant message with a unique streamId:
1const persistentTextStreaming = new PersistentTextStreaming(
2 components.persistentTextStreaming
3);
4
5export const sendMessage = mutation({
6 args: { conversationId: v.id("conversations"), content: v.string() },
7 handler: async (ctx, args) => {
8 const userId = await getAuthUserId(ctx);
9 if (!userId) throw new Error("Not authenticated");
10
11 const conversation = await ctx.db.get("conversations", args.conversationId);
12 if (!conversation || conversation.userId !== userId) {
13 throw new Error("Conversation not found");
14 }
15
16 // Insert user message
17 const userMessageId = await ctx.db.insert("messages", {
18 conversationId: args.conversationId,
19 role: "user",
20 content: args.content,
21 });
22
23 // Create a stream for the AI response
24 const streamId = await persistentTextStreaming.createStream(ctx);
25
26 // Create the AI message with streaming enabled
27 const aiMessageId = await ctx.db.insert("messages", {
28 conversationId: args.conversationId,
29 role: "assistant",
30 content: "", // Start with empty content
31 streamId: streamId,
32 isStreaming: true,
33 });
34
35 // Update conversation timestamp
36 await ctx.db.patch("conversations", args.conversationId, {
37 lastMessageAt: Date.now(),
38 });
39
40 return {
41 userMessageId,
42 aiMessageId,
43 streamingMessageId: aiMessageId,
44 streamId: streamId
45 };
46 },
47});
48The streamId is saved alongside the assistant message, and the frontend can use it with useStream to subscribe to live updates.
2. Consuming Streams in React
On the frontend, query the messages and display those with a streamId using a streaming component:
1import React from "react";
2import { useQuery } from "convex/react";
3import { api } from "../../convex/_generated/api";
4import StreamingMessage from "./StreamingMessage";
5
6const MessageList: React.FC<{ conversationId: string }> = ({
7 conversationId,
8}) => {
9 const messages = useQuery(api.chat.getMessages, { conversationId });
10
11 return (
12 <div className="message-list">
13 {messages?.map((message) => (
14 <div key={message._id} className={`message ${message.role}`}>
15 {message.role === "assistant" && message.streamId ? (
16 <StreamingMessage message={message} />
17 ) : (
18 <div className="whitespace-pre-wrap break-words">
19 {message.content}
20 </div>
21 )}
22 </div>
23 ))}
24 </div>
25 );
26};
27Messages with a streamId are displayed using the StreamingMessage component. Once streaming completes, the final text is saved and rendered as part of the conversation. Regular messages are shown as usual.
With this structure:
- The backend issues a
streamIdand creates a placeholder assistant message. - A streaming action progressively writes the AI response.
- The frontend subscribes to updates using the
streamId.
This pattern enables a ChatGPT-style, real-time chat experience built on Convex.
With this pattern in place, you can create a fully interactive, real-time AI chat experience in Convex without handling SSE or WebSocket logic manually.

The final result: Real-time streaming responses that create an engaging, ChatGPT-like experience for your users.
Simplify Your Real-Time Features Using Pre-Built, Reusable Components
Convex Components turn complex real-time features into simple, reusable modules. With @convex-dev/persistent-text-streaming, we've built a production-ready streaming chat interface without dealing with low-level protocols.
Key takeaways:
- Convex Components abstract away infrastructure complexity
- Real-time streaming is as simple as installing a package and using a React hook
- The pattern of backend stream creation + frontend consumption scales to any streaming use case
What's next?
- Explore other Convex Components for features like auth, payments, and more
- Check out the Convex documentation for advanced patterns
- Join the Convex Discord to share your streaming implementations
Convex is the backend platform with everything you need to build your full-stack AI project. Cloud functions, a database, file storage, scheduling, workflow, vector search, and realtime updates fit together seamlessly.